Pile Location Detection
Nondestructive pile location detection
Pile layout Detection
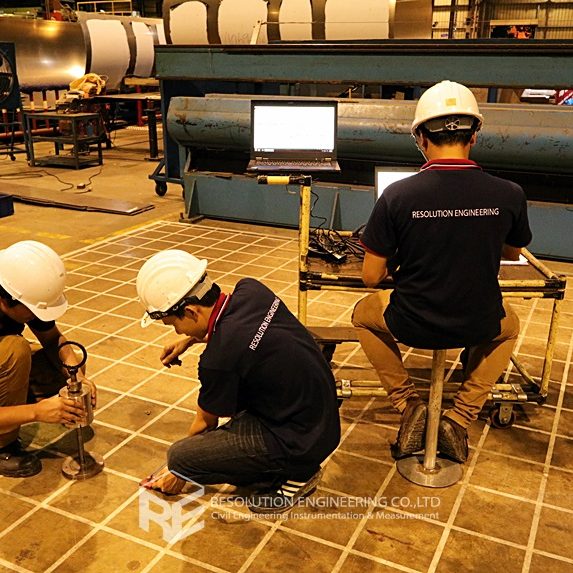
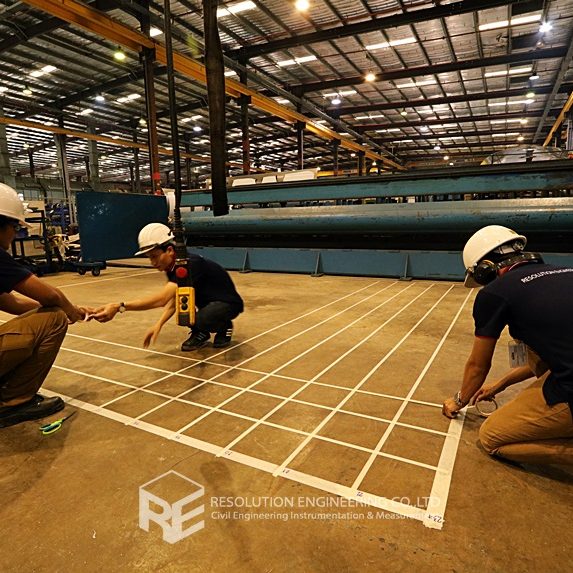
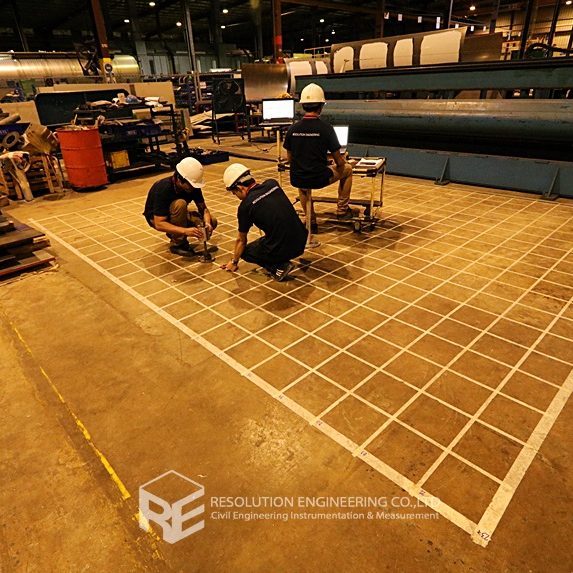
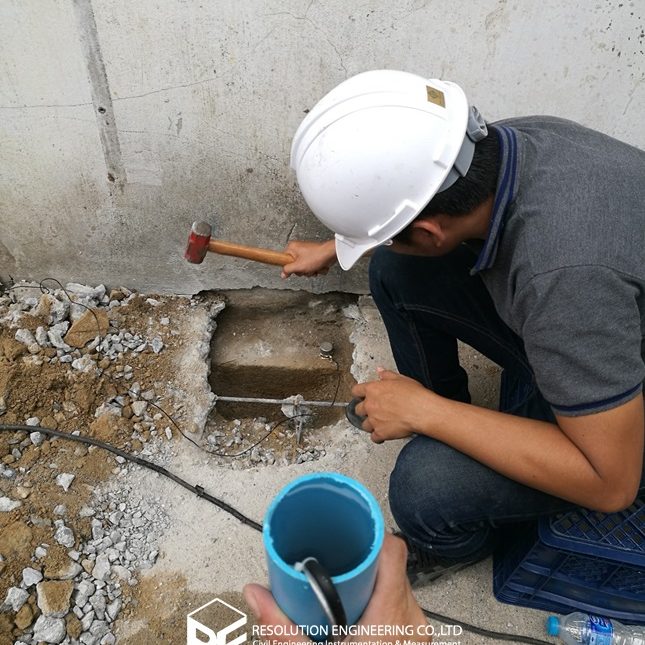
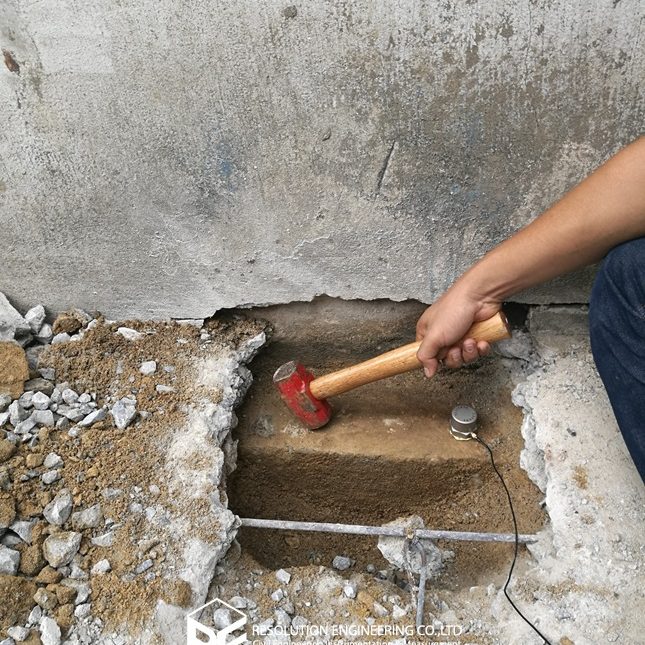
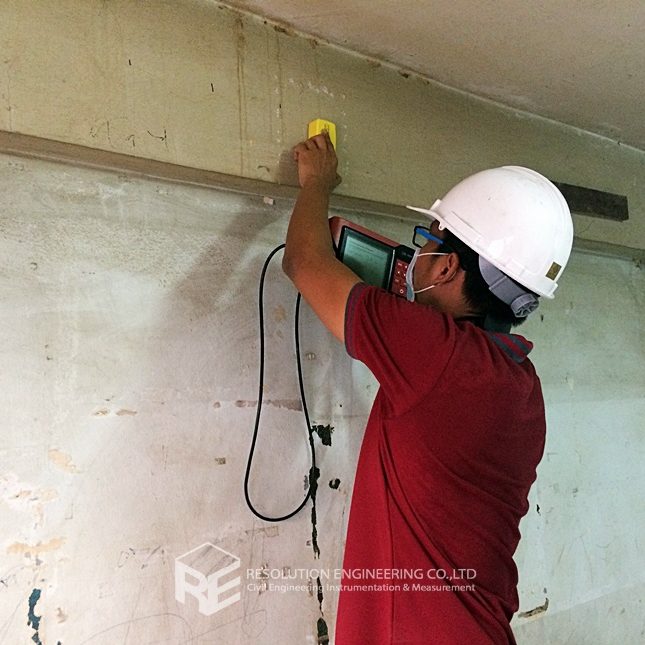
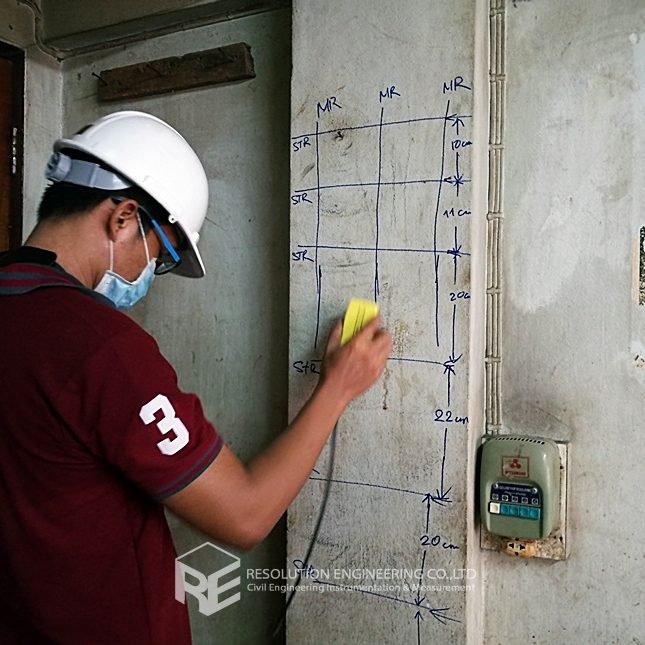
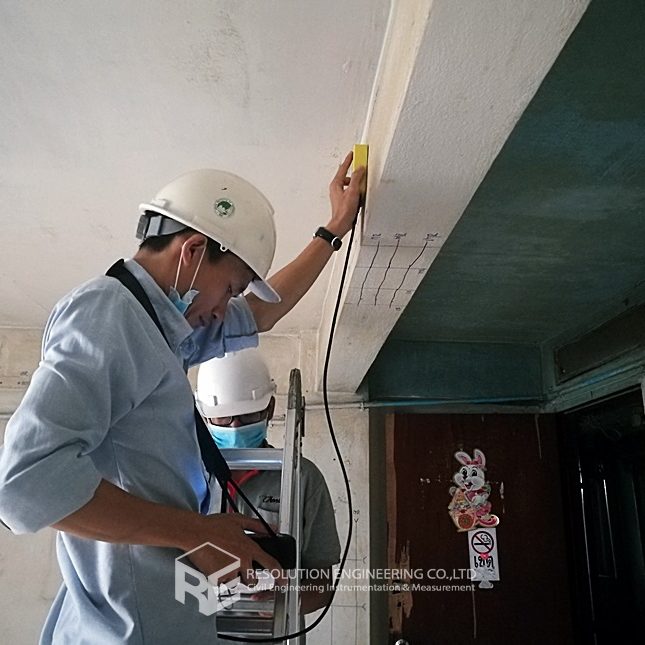
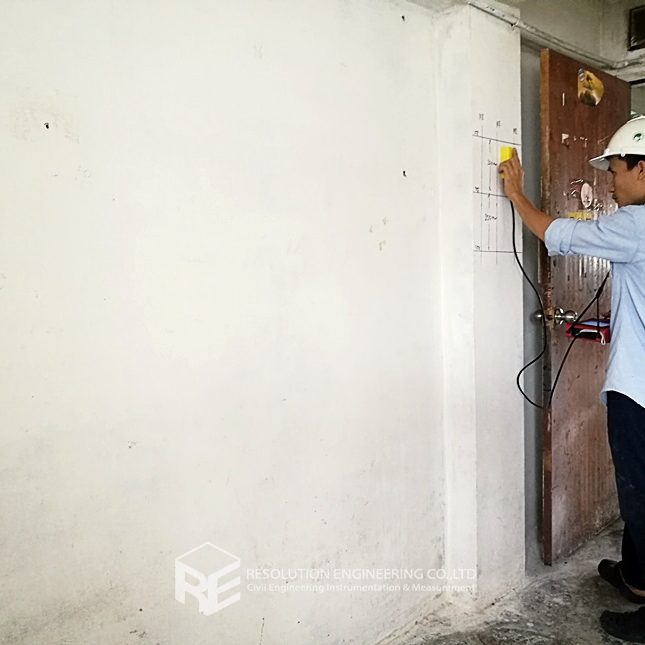
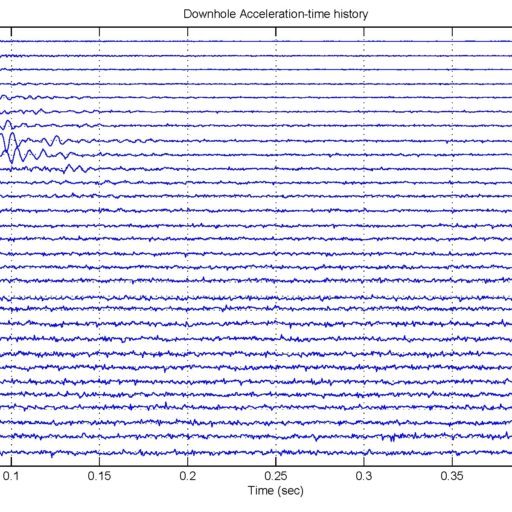
One very common problem is that the drawing or evidence of the floor pile layout or location is missing. As a result, a thorough floor capacity analysis cannot be done. Load carrying capacity also cannot be verified. When dealing with one of these cases, RE team conducted the Non-Destructive Pile Detection on the concrete floor of a factory in the Bangpa-In Industrial Estate. This factory was built a long time ago, and the pile location and layout no longer exist. By means of seismic waves generated from a drop hammer and received by accelerometers via a dynamic data logging system, the acceleration record was analyzed, and the pile location was determined.